Diabetes Treatment
Diabetes is a common condition that affects people of all ages. There are several forms of diabetes. Type 2 is the most common. A combination of treatment strategies can help you manage the condition to live a healthy life and prevent complications.
Management and Treatment
How is diabetes managed?
Diabetes is a complex condition, so its management involves several strategies. In addition, diabetes affects everyone differently, so management plans are highly individualized.
The four main aspects of managing diabetes include:
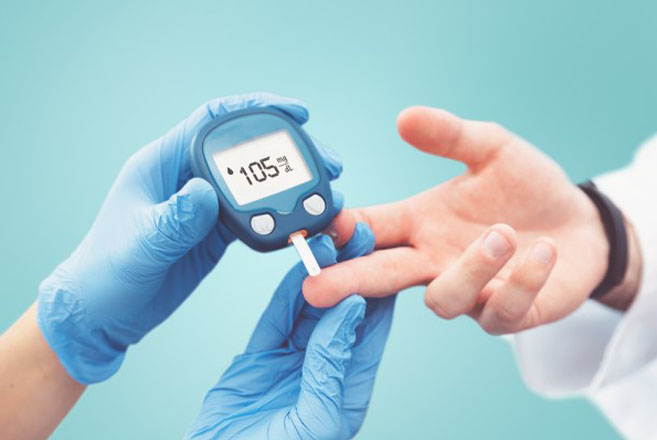
- Blood sugar monitoring: Monitoring your blood sugar (glucose) is key to determining how well your current treatment plan is working. It gives you information on how to manage your diabetes on a daily — and sometimes even hourly — basis. You can monitor your levels with frequent checks with a glucose meter and finger stick and/or with a continuous glucose monitor (CGM). You and your healthcare provider will determine the best blood sugar range for you.
- Oral diabetes medications: Oral diabetes medications (taken by mouth) help manage blood sugar levels in people who have diabetes but still produce some insulin — mainly people with Type 2 diabetes and prediabetes. People with gestational diabetes may also need oral medication. There are several different types. Metformin is the most common.
- Insulin: People with Type 1 diabetes need to inject synthetic insulin to live and manage diabetes. Some people with Type 2 diabetes also require insulin. There are several different types of synthetic insulin. They each start to work at different speeds and last in your body for different lengths of time. The four main ways you can take insulin include injectable insulin with a syringe (shot), insulin pens, insulin pumps and rapid-acting inhaled insulin.
- Diet: Meal planning and choosing a healthy diet for you are key aspects of diabetes management, as food greatly impacts blood sugar. If you take insulin, counting carbs in the food and drinks you consume is a large part of management. The amount of carbs you eat determines how much insulin you need at meals. Healthy eating habits can also help you manage your weight and reduce your heart disease risk.
- Exercise: Physical activity increases insulin sensitivity (and helps reduce insulin resistance), so regular exercise is an important part of management for all people with diabetes.
Due to the increased risk for heart disease, it’s also important to maintain a healthy:
- Weight.
- Blood pressure.
- Cholesterol.